Why Customer Segmentation is important
Knowing your potential customers is the first driver that business owners should be interested in, and using precise segmentations to divide customers into categories can make a huge difference.
Imagine having different segmentations of your customer base at your disposal; you can build advertising campaigns closely related to each segment's different needs and behaviours, increasing the Click Through Rate and, consequently, the Conversion Rate in general by several percentage points.
Customer segmentation is a process that clarifies and classifies all customers into well-defined clusters with appropriate rules for each type. Basically, if our best-seller segment consists of women between 45 and 55 years old for cosmetic products, it would be appropriate not to target advertising to men between 30 and 35 years old. This, like so many other variables, falls within customer segmentation logic.
What are the main benefits of customer segmentation?
- Improving Customer Retention
- Increase the value of the individual customer over time
- Exponentially increase the ROI from individual marketing campaigns.
If you are not currently using customer segmentation, now is the time to start and reap the valuable benefits of this work.
Who are the customers in your market
The customer is the beating heart of every business activity. Segmenting customers to know them more deeply is, therefore, a must for anyone who would like to give their business an extra boost
Not all customers are the same; the greater the heterogeneity of customers, the greater the clusters to be organized in customer segmentations. If the good/service we sell, for example, targets a very large audience, it goes without saying that the segmentation will certainly be more complex and larger.
However, there are some basic concepts to keep in mind whenever we create and use audience segments:
Criteria
Identifies the exact criteria based on which to carry out segmentation. How old are my regular customers? What language do they speak? With what type of device do they interact with our business when they are online?
Keep things simple
Don't try to segment the same users in so many different ways. Just use some basic concepts once to cluster the entire customer base at your disposal.
Be Specific
The more specific you can be in each cluster the more truthful you can be in perfectly intercepting their needs.
Test & Iterate
The testing phase is undoubtedly crucial when dealing with customer segmentation. We may have everything conceptually ready, but at the time of testing not receive the desired results. This phase is very important since if the tests are brilliantly passed the same can be repeated in all contexts and generate exponentially higher gains.
Defining Your Segments
But what kind of clustering can we implement? In this section, we go into detail regarding the types of segmentation that can be created and what type they may be:
Behaviour: Based on user navigation or purchasing history. How do they manage to interact with our company? In this cluster, we highlight, for example, the purchase history made by a user or the degree of interaction with the website (bounce rate, time spent on the site, pages visited per session, etc)
Needs: Intercepting customer needs is perhaps the most complex segmentation to do because, at its core, it has both qualitative and quantitative variables. A good interest prediction system must consider certain variables, such as users of related segments or products and the browsing history of each user, by proposing remarketing activities.
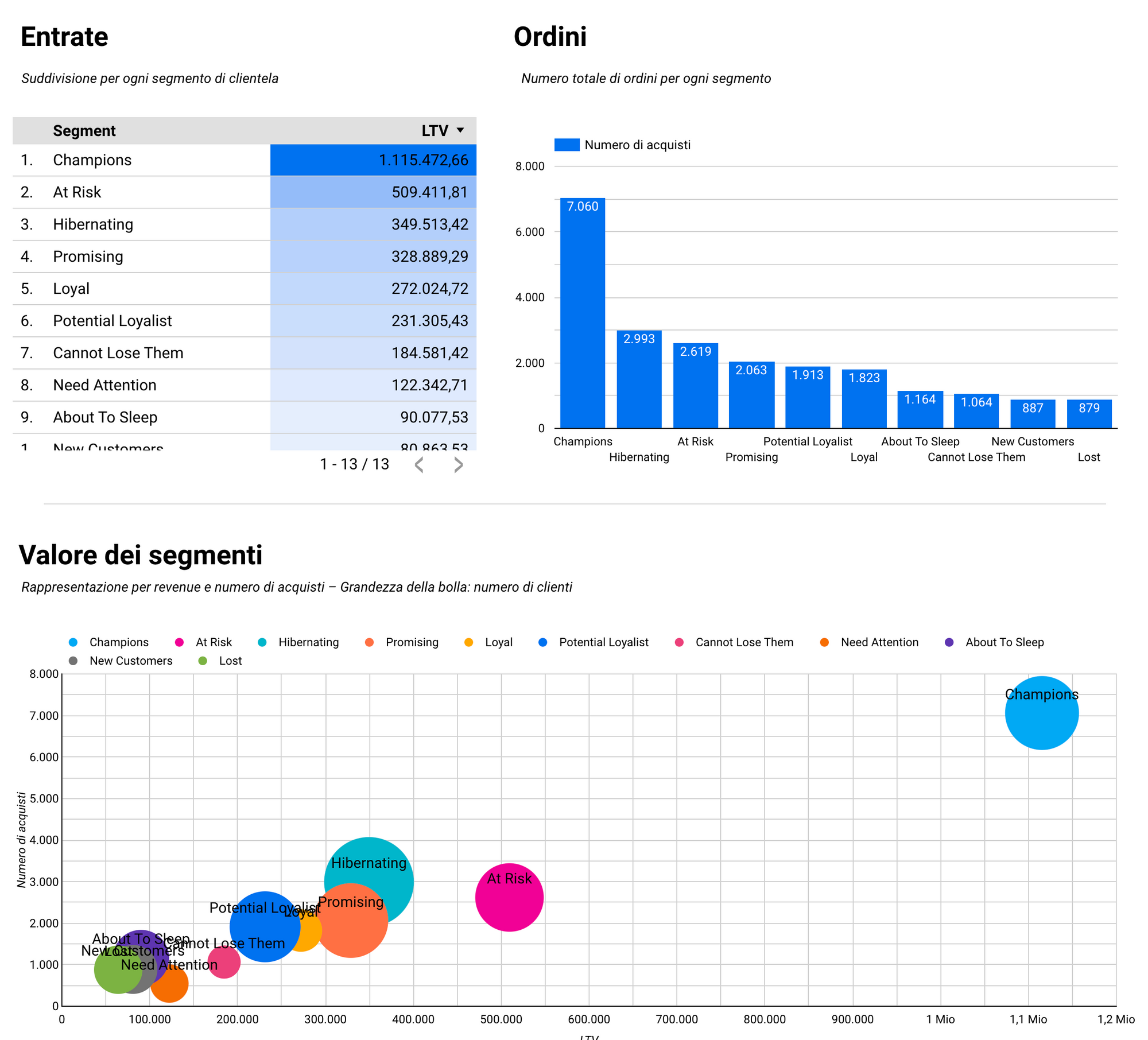
You can download a FREE Google Data Studio for RFM analysis by clicking here.
Engagement Strategy using customer segmentation
Customer segmentation is used in many ways within a company's promotional activities. Certainly, the most immediate possibility is to use predefined clusters to target the campaign most akin to their needs.
There are several successful campaigns in which customer segmentation resulted in a real sales boom. Think, for example, of those who have practically always enjoyed large budgets for online advertising campaigns but have never clustered users: a large part of this budget will inevitably be lost because it is directed toward users who have no interest in our business. Ultimately, customer segmentation should also be understood as a highly positive factor in rationalizing advertising investments to make them more effective.
Implementing an effective engagement strategy using customer segmentation is crucial for businesses aiming to deliver personalized experiences, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive long-term loyalty. By segmenting customers based on common characteristics, behaviours, and preferences, businesses can tailor their engagement strategies to meet the unique needs of each segment. Here are some examples of how businesses can leverage customer segmentation to enhance their engagement strategies:
Example 1: E-commerce Retailer

An e-commerce retailer segments its customer base based on purchase history, browsing behavior, and demographic information. Through careful analysis, the retailer identifies several distinct segments, including:
- Frequent Shoppers: Customers who make regular purchases and exhibit high brand loyalty.
- Occasional Buyers: Customers who make infrequent purchases or have only made one-time purchases.
- Deal Seekers: Customers motivated by discounts, promotions, and special offers.
- High-Value Customers: Customers who spend significantly more than average and are likely to be brand advocates.
To engage each segment effectively, the retailer develops targeted strategies:
- For Frequent Shoppers: Implement a loyalty program with exclusive rewards, early access to new products, and personalized recommendations based on past purchases.
- For Occasional Buyers: Send targeted email campaigns highlighting new products, limited-time promotions, and personalized discounts to encourage repeat purchases.
- For Deal Seekers: Launch flash sales, limited-time offers, and clearance events to incentivize immediate purchases and create a sense of urgency.
- For High-Value Customers: Provide personalized VIP treatment, such as dedicated account managers, priority customer service, and invitation-only events.
By tailoring engagement strategies to each customer segment's specific needs and preferences, the e-commerce retailer can foster deeper connections, drive repeat purchases, and maximize customer lifetime value.
Example 2: Financial Institution
A financial institution segments its customer base into different groups based on financial needs, life stages, and channel preferences. The segments identified include:
- Savers and Investors: Customers who prioritize saving and investment products, such as savings accounts, CDs, and mutual funds.
- Borrowers: Customers who require financing solutions, including mortgages, personal loans, and credit cards.
- High Net Worth Individuals: Customers with substantial assets and complex financial needs, such as wealth management services, estate planning, and investment advisory.
- Digital Savvy Millennials: Younger customers who prefer digital banking channels, mobile apps, and online financial management tools.
To engage each segment effectively, the financial institution tailors its strategies:
- For Savers and Investors: Offer competitive interest rates, flexible investment options, and educational resources to help customers achieve their financial goals.
- For Borrowers: Provide personalized loan offers, refinancing options, and financial counseling to support borrowers throughout their financial journey.
- For high-net-worth individuals: Offer personalized wealth management services, investment advice, and exclusive benefits to cater to their sophisticated financial needs.
- For Digital Savvy Millennials: Enhance digital banking capabilities, streamline account opening processes, and develop mobile-friendly interfaces to meet the preferences of tech-savvy customers.
By understanding each customer segment's unique needs and preferences, the financial institution can deliver targeted solutions, strengthen customer relationships, and drive engagement across various touchpoints.
Customer segmentation is a powerful tool for businesses to develop tailored engagement strategies that resonate with their diverse customer base. By understanding each segment's distinct characteristics and preferences, businesses can deliver personalized experiences, foster stronger connections, and drive meaningful interactions that ultimately drive business growth and success.
Frequently Asking Questions about Customer Segmentation
What is Customer Segmentation?
Customer segmentation divides a customer base into distinct groups or segments based on common characteristics, behaviors, and preferences. This strategic approach allows businesses to understand their customers better and tailor marketing efforts, products, and services to meet the specific needs of each segment. By segmenting customers, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, improve targeting accuracy, and drive more effective marketing campaigns.
What is the Meaning of Customer Segmentation?
Customer segmentation is categorizing customers into homogeneous groups based on shared traits or attributes. These traits can include demographic factors such as age, gender, income level, and geographic location, as well as psychographic variables like lifestyle, values, attitudes, and purchasing behaviour. By segmenting customers, businesses can gain deeper insights into their diverse customer base and effectively tailor their strategies to meet each segment's unique needs and preferences.
What is the Customer Segmentation Definition?
The definition of customer segmentation encompasses dividing a customer base into distinct segments or groups based on identifiable characteristics, behaviors, or attributes. These segments enable businesses to categorize customers according to common traits, preferences, and needs, allowing for more targeted marketing, personalized communication, and improved customer experiences. By implementing effective customer segmentation strategies, businesses can enhance customer engagement, drive loyalty, and achieve greater success in their marketing efforts.
What are the Customer Segmentation Types?
There are several types of customer segmentation commonly used by businesses to categorize their customer base:
- Demographic Segmentation: Dividing customers based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education level, marital status, and occupation.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Grouping customers according to lifestyle, personality traits, values, beliefs, interests, and attitudes.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Segmenting customers based on their purchasing behavior, usage patterns, brand loyalty, product preferences, and buying frequency.
- Geographic Segmentation: Dividing customers by geographic location, such as country, region, city, climate, population density, or urban/rural areas.
Each type of segmentation offers unique insights into customer behavior and preferences, allowing businesses to tailor their marketing strategies and offerings to target and engage specific customer segments effectively. By leveraging customer segmentation, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts, improve customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
